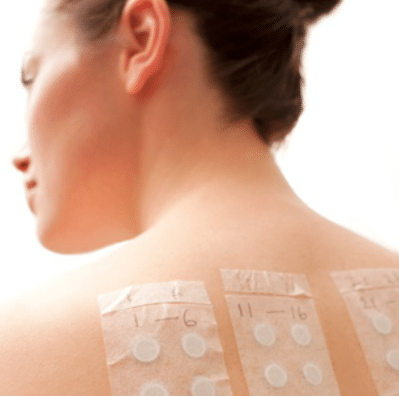
Patch testing is a common diagnostic tool used to identify the specific agent that triggers allergic contact dermatitis. This testing does not involve needles or injections.
Common substances to cause allergic skin rashes include preservatives in cosmetics, cleaning solutions, detergents, and fragrance.
Common symptoms of allergic contact dermatitis include redness, blisters, itching, rash, and hives.
These symptoms can last for up to four weeks, and can usually be treated at home through medications and topical creams. The best protection against contact dermatitis is to identify the specific triggers that cause reactions, so that patients can avoid these substances as often as possible. A patch test may help identify the trigger. It does not require the use of any needles or injections.
Most dermatologists use the TRUE Test.
In order to identify specific triggers, your doctor will tape several patches that contain various potential chemicals to the skin on the back. These chemicals are then left on the skin for 48 hours, and must remain dry during this time. Patients are advised to take only sponge baths and avoid excessive sweating. After 48 hours, the patch test is removed and an initial reading is taken to observe any reactions. An additional reading may be taken after another 24-48 hours.
Once positive results have been determined, patients can take steps to avoid their triggers and prevent contact dermatitis from occurring. Your doctor will provide you with specific information on your individual triggers and how to prevent contact.